Task description
Paraphrase can be defined as “the same meaning of a sentence is expressed in another sentence using different words”. Paraphrases can be identified, generated or extracted. The proposed task is focused on sentence level paraphrase identification for Indian languages (Tamil, Malayalam, Hindi and Punjabi). Identifying paraphrases in Indian languages is a difficult task, because evaluating the semantic similarity of the underlying content and the understanding the morphological variations of the language are more critical. Paraphrase identification is strongly connected with generation and extraction of paraphrases. The paraphrase identification systems improve the performance of a paraphrase generation in terms of choosing the best paraphrase candidate from the list of paraphrases candidates generated by paraphrases generation system. Paraphrase Identification is also used in validating the paraphrase extraction system and the machine translation system. In QA system, Paraphrase Identification plays a vital role in matching the questions asked by the user to the original questions for choosing the best answer. Plagiarism detection is another task which needs the Paraphrase Identification technique to detect the sentences which are paraphrases of others.
One of the most commonly used corpora for paraphrase detection is the MSRP corpus (Dolan and Brockett 2005), which contains 5,801 English sentence pairs from news articles manually labelled with 67% paraphrases and 33% non-paraphrases. Since there are no annotated corpora or automated semantic interpretation systems available for Indian languages till date, creating benchmark data for paraphrases and utilizing that data in open shared task competitions will motivate the research community for further research in Indian languages.
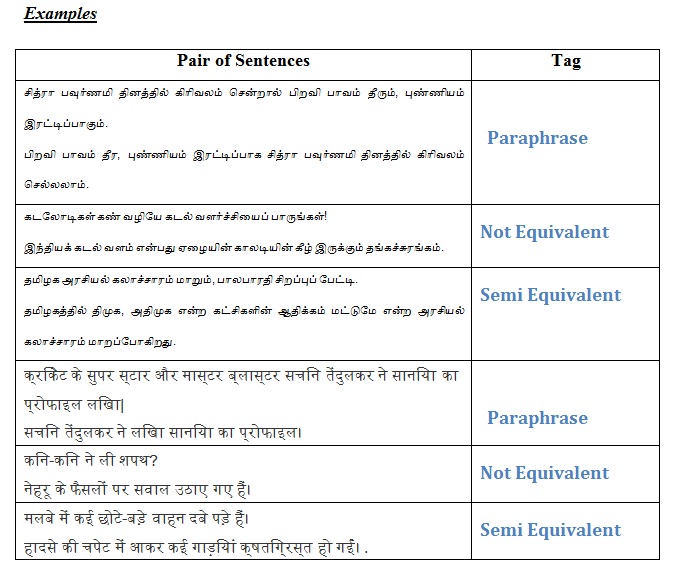
Sub Task 1: Given a pair of sentences from news paper domain, the task is to classify them as paraphrases (P) or not paraphrases (NP).
Sub Task 2: Given two sentences from news paper domain, the task is to identify whether they are completely equivalent (E) or roughly equivalent (RE) or not equivalent (NE). This task is similar to the subtask 1, but the main difference is 3-point scale tag in paraphrases.
USECASES
1. Automatic paraphrasing for Indian languages
2. Semantic similarity between sentences and documents
3. Summarization and Text entailment.
4. Plagiarism detection for Indian Languages.
Output format

Registration
Registration closed,
Dataset
Important Dates
Training Data Release
Test Data Release
Run Submission Deadline
Results Declared
Working Notes Due
Conference
evaluation and results
To see results, check here
Updates
- 1. Fill the Data use agreement form and send it to dpil_cen@cb.amrita.edu
- 2. Tamil and Malayalam train data released on 15th July 15th July
- 3. Registration ends on 25th July
- 4. Training data for Hindi and Punjabi were released
- 5. More than 35 teams were registered for this Shared task
- 6. Details about Sarwan awrads were released
- 7. Testing data released
- 8. Output format for result submission released.
| Anand Kumar M, CEN, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore, India |
| Soman K P , CEN, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore, India |
Prof. Ramanan, RelAgent Pvt Ltd, Chennai
Prof. N. Deiva Sundaram, NDS Lingsoft Solutions Pvt. Ltd., Chennai
Prof. Rajendran S, CEN, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore, India
Dr. V. Dhanalakshmi, Assistant Director, Tamil Virtual Academy,Chennai
Dr. Govind D , CEN,Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham
Mr. Vijay Krishnan Menon ,CEN,Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham
Mr. Barathi Ganesh , Data Science practitioner,TCS Cochin